
An Overview of the Handle System
William Y. Arms
Corporation for National Research Initiatives
Slides from the Handle Server workshop.
Reston VA.
July 27 and 28,1995.
Desirable Properties of Identifiers
- Location independent name
- Globally unique
- Persistent across time
- Choice of human generated or automatic generation
- Fast resolution
- Decentralized administration
- Change control
- Supported from standard user interfaces
General Philosophy
We can not dictate the variety of applications that the handle system must support.
Therefore, we build general purpose system components that will support great variety of systems and applications.
A handle is a pure name. No assumptions are built into the system about the type of object, the use made, or the applications.
Syntax
Syntax
naming_authority / locally_unique_string
or
hdl:// naming_authority / locally_unique_string
Examples
- date-time stamp
- cnri.xiwt.rbb/1995.02.12.16.42.21;9
- mnemonic name
- berkeley.cs/ucb-cstr-94.45
- random string
- loc/a43v-8940cgr
Elements of the Handle System
- Naming authorities
handle generators
- Handle services:
- global handle service
- local handle services
- caching services
- Clients:
- client libraries
- WWW proxy servers
- Handle administration
- System utilities
Hierarchy of Naming Authorities
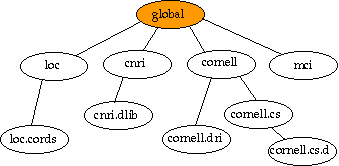
Handle Services are Non-Hierarchical
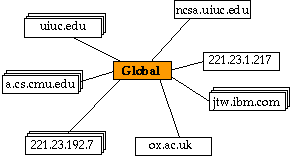
Handle Servers and Handle Service
Each handle service may be implemented as several handle servers.
A hashing algorithm determines the server used to store a given handle.
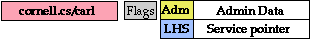
The Handle Record
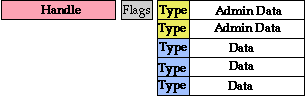
Example 1
Handle Record for an Internet Object
"Object Handle"
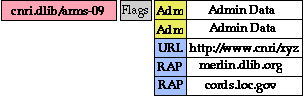
Example 2
Handle Record for a Naming Authority
"Authority Handle"

Note: The form of handle for a naming authority is
under review.
Example 3
Handle Record for a Local Handle Server
"Service Handle"
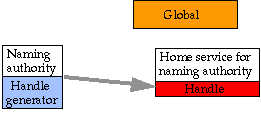
Creation of a Naming Authority
The parent naming authority, creates a record in the global handle server containing, for the new authority:
- the name of the naming authority
- the home handle server
- the ID of the administrator(s)
Example 1: Creating a New Handle
in the Home Handle Service
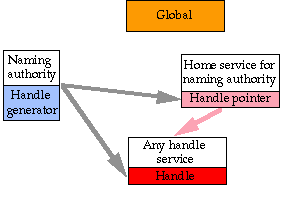
Example 2: Creating a New Handle
in Any Handle Server
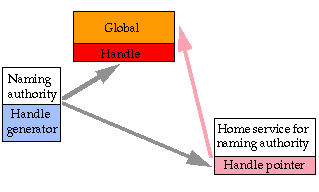
Example 3: Creating a New Handle
in the Global Handle Server
Address Rules
- The Global Handle Service stores:
- a record for each naming authority.
a record for each local handle service
- The record for each naming authority includes:
- the home handle service for that naming authority.
- For each handle, the primary handle service stores:
- either the handle record,
or a pointer to the handle service that stores the handle record.
Resolving a Handle Without Caches
Example 1: Handle, cnri.dlib/wya,
in Global, G
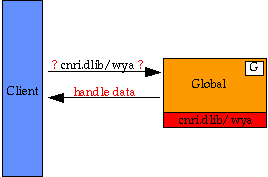
Resolving a Handle Without Caches
Example 2: Handle, cnri.dlib/wya,
in Home Service, abc
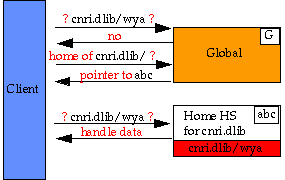
Resolving a Handle Without Caches
Example 3: Handle, cnri.dlib/wya,
in Handle Service, xyz
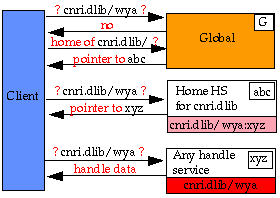
Caching Handle Service
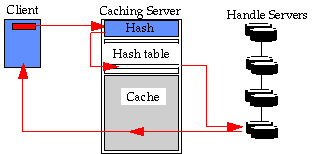
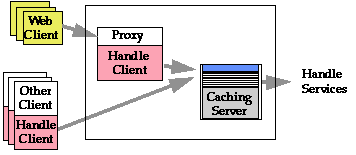
Possible Client Configuration
for an Organization
Click here for further information on Handles and the Handle System.
The Handle System was developed as part of the
Computer Science Technical Reports project. Funding has been provided by ARPA and the Library of Congress.
wya
August 2, 1995















